| Table 1. Relationship between seed hair and embryo development in ((Populus pseudo simonii × P. nigra ‘Zheyin3#’) × (P. × beijingensis)) ovaries. | ||||||||
| Defined stages | Developmental characteristics of seed hair | Percentage of each developmental stage (%) | ||||||
| Developing embryo sac | Mature embryo sac and double fertilization | Hypnozygote | 2-celled embryo | 4-celled embryo | 8-celled embryo | >8-celled embryo | ||
| I | No hair forms | 83.72 (36) a) | 16.28 (7) | |||||
| II | Development of the hair initiates around the funiculus | 23.68 (9) | 63.16 (24) | 13.16 (5) | ||||
| III | The hair gradually elongates to cover the funiculus | 36.36 (16) | 56.82 (21) | 6.82 (3) | ||||
| IV | The hair begins to enclose the ovules | 44.44 (20) | 37.78 (17) | 15.56 (7) | 2.22 (1) | |||
| V | The hair encloses the ovules completely, but does not fill the ovary | 9.52 (4) | 26.19 (11) | 38.10 (16) | 21.43 (9) | 4.76 (2) | ||
| VI | The hair fills the ovary | 18.37 (9) | 34.69 (17) | 46.94 (23) | ||||
| a) Number of observed ovules. | ||||||||
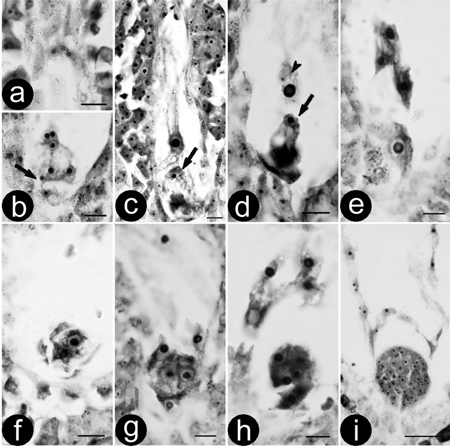
Fig. 1. Double fertilisation and zygote development of (P. pseudo-simonii × P. nigra ‘Zheyin3#’) × (P. × beijingensis). a-b) Serial sections showing a mature embryo sac and two sperms (arrow); c) Movement of the sperm, arrow showing a sperm is close to the egg; d) Double fertilisation, one sperm is fusing to the egg (arrow) and the other to central cell (arrow head); e) Zygote; f) Two-celled embryo; g) Four-celled embryo; h) Eight-celled embryo; i) Globular embryo. Bars are equal to 10 μm in a–h and 50 μm in i.

Fig. 2. Development of seed hairs in the ovaries: a) Stage I ovary without hair formation; b) Stage II ovary, indicating initiation of hairs around the funiculus; c) Stage III ovary, characterised by hair elongation gradually covering the funiculus; d) Stage IV ovary with hairs enclosing the ovules; e) Stage V ovary not filled by hairs, but completely enclosed ovules; f) Stage VI ovary filled by hairs.
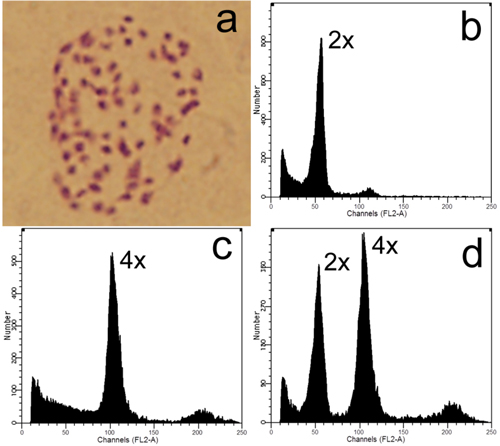
Fig. 3. Ploidy level detection of offspring derived from zygotic chromosome doubling: a) Somatic chromosome of a tetraploid (2n = 4x = 76); b–c) Flow cytometric analyses of a diploid and tetraploid, respectively; d) Histogram of flow cytometric analysis of nuclei mixture of young leaves from the former diploid and tetraploid plants.
| Table 2. Tetraploid production through colchicine-induced zygotic chromosome doubling in (P. pseudo-simonii × P. nigra ‘Zheyin3#’) × (P. × beijingensis) hybrids. | |||||||
| Stage of seed hair development | Concentration of colchicine solution (%) | Duration of treatment (h) | No. of catkins | No. of seeds | No. of seedlings | No. of tetraploids | Efficiency of tetraploid production (%) |
| II | 0.3 | 24 | 2 | 124 | 58 | 1 | 1.72 |
| 0.5 | 24 | 2 | 108 | 39 | 1 | 2.56 | |
| III | 0.3 | 24 | 3 | 248 | 174 | 2 | 1.15 |
| 0.5 | 24 | 2 | 104 | 64 | 2 | 3.13 | |
| IV | 0.3 | 24 | 2 | 36 | 6 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.5 | 24 | 2 | 78 | 28 | 0 | 0 | |
| V | 0.3 | 24 | 2 | 85 | 27 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.5 | 24 | 2 | 79 | 37 | 0 | 0 | |
| Control | 2 | 417 | 240 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Table 3. Tetraploid production through high-temperature-induced zygotic chromosome doubling in (P. pseudo-simonii × P. nigra ‘Zheyin3#’) × (P. × beijingensis) hybrids. | |||||||
| Stage of seed hair development | Temperature (°C) | Duration of treatment (h) | No. of catkins | No. of seeds | No. of seedlings | No. of tetraploids | Efficiency of tetraploid production (%) |
| II | 39 | 2 | 2 | 132 | 74 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | 3 | 172 | 84 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 6 | 2 | 153 | 72 | 1 | 1.39 | ||
| 41 | 2 | 3 | 217 | 112 | 0 | 0 | |
| 4 | 3 | 232 | 122 | 1 | 0.82 | ||
| 6 | 4 | 341 | 295 | 1 | 0.34 | ||
| 43 | 2 | 2 | 106 | 32 | 0 | 0 | |
| 4 | 2 | 24 | - | - | - | ||
| 6 | 2 | 17 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| III | 39 | 2 | 3 | 208 | 137 | 3 | 2.19 |
| 4 | 3 | 254 | 142 | 2 | 1.41 | ||
| 6 | 2 | 131 | 81 | 2 | 2.47 | ||
| 41 | 2 | 3 | 219 | 120 | 0 | 0 | |
| 4 | 2 | 137 | 42 | 1 | 2.38 | ||
| 6 | 2 | 147 | 44 | 2 | 4.55 | ||
| 43 | 2 | 2 | 114 | 26 | 0 | 0 | |
| 4 | 2 | 13 | - | - | - | ||
| 6 | 2 | - | - | - | - | ||
| IV | 39 | 2 | 2 | 80 | 21 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | 2 | 155 | 92 | 1 | 1.09 | ||
| 6 | 2 | 177 | 118 | 3 | 2.54 | ||
| 41 | 2 | 2 | 149 | 97 | 2 | 2.06 | |
| 4 | 2 | 73 | 23 | 1 | 4.35 | ||
| 6 | 2 | 74 | 36 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 43 | 2 | 2 | 101 | 27 | 2 | 7.41 | |
| 4 | 2 | 24 | - | - | - | ||
| 6 | 2 | - | - | - | - | ||
| V | 39 | 2 | 3 | 182 | 80 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | 2 | 130 | 53 | 1 | 1.89 | ||
| 6 | 2 | 79 | 22 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 41 | 2 | 2 | 138 | 77 | 1 | 1.3 | |
| 4 | 2 | 83 | 22 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 6 | 2 | 105 | 50 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 43 | 2 | 2 | 125 | 86 | 1 | 1.16 | |
| 4 | 2 | 57 | 14 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 6 | 2 | - | - | - | - | ||
| Control | 2 | 476 | 256 | 0 | |||
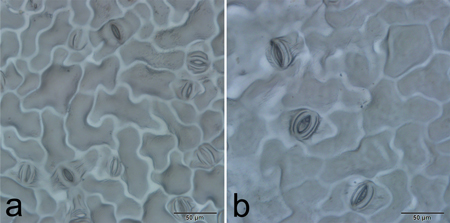
Fig. 4. Stomatal size and frequency of diploid (a) and tetraploid (b) plants.
| Table 4. Stomatal characteristics of diploid and tetraploid (P. pseudo-simonii × P. nigra ‘Zheyin3#’) × (P. × beijingensis) offspring. | ||||||
| Characters | Tetraploids | Diploids | t-value | P-value | ||
| Range | Mean ± SE | Range | Mean ± SE | |||
| Stomata length (μm) | 31.9–42.6 | 37.6 ± 0.4 | 24.3–33.2 | 28.9 ± 0.5 | 14.350** | <0.0001 |
| Stomata width (μm) | 18.0–23.5 | 20.4 ± 0.2 | 15.0–19.8 | 17.1 ± 0.2 | 10.178** | <0.0001 |
| Stomatal frequency (mm–2) | 57.7–180.6 | 113.6 ± 5.4 | 146.7–294.3 | 219.6 ± 7.7 | 11.142** | <0.0001 |
| ** Significant differences between diploids and tetraploids at α = 0.01 in t-test. | ||||||