Fig. 1. A typical planting stick (left), consisting of a wooden rod with an iron planting tip, and iron wire with bolts indicating precise planting spots. Photo on the right shows a worker in the middle stretching a wire line to prepare the next row, a worker on the left waiting for her turn, and a worker on the right doing actual planting and soil compaction work.
| Table 1. Description of work elements of the two planting methods. |
| Method | Work phases | Work elements | Description |
Planting
stick | Preparation | Moving | Begins when the worker starts walking towards a new location and ends when s/he reaches it |
| Aligning | Begins when the worker starts looking at colleagues to set the marking chains perpendicular to each other (visually) and ends when workers have finished putting marking sticks in the ground |
| Planting | Walking | Begins when the worker starts walking to a marked location and ends when s/he reaches it |
| Preparing | Begins when the worker puts a planting stick in the soil and ends when s/he moves to the next spot |
| Planting | Begins when the worker takes a seedling from his/her bag and ends when s/he is back in the standing position |
| Tamping | Begins when the worker starts to compact the soil by foot and ends when s/he is ready to move on |
Planting
tube | Preparation | Measuring | Begins when the worker starts to measure the correct distance for the next row from the previous row and ends when the location is defined |
| Walking | Begins when the worker starts walking towards the new location of a marking stick and ends when s/he reaches it |
| Locating | Begins when the worker puts a marking stick in the ground and ends when it is checked and corrected, to ensure that it is parallel with others |
| Moving | Begins when the worker starts to walk ahead of a marking stick to the next location and ends when s/he reaches it |
| Planting | Walking | Begins when the worker starts walking to a planting spot and ends when s/he reaches the spot |
| Preparing | Begins when the worker presses the planting tube to the ground and ends when the jaws are opened |
| Planting | Begins when the worker moves his/her hand to the basket and ends when a seedling is dropped out of the tube |
| Pulling up | Begins when the worker starts to pull up the tube and ends when the jaws are closed |
| Tamping | Begins when the worker compacts soil by foot and ends when s/he is ready to move on |
| Navigating | Begins when the worker sets the tube next to the planted seedling and ends when s/he lifts up the tip of the dimension stick from the next planting spot |
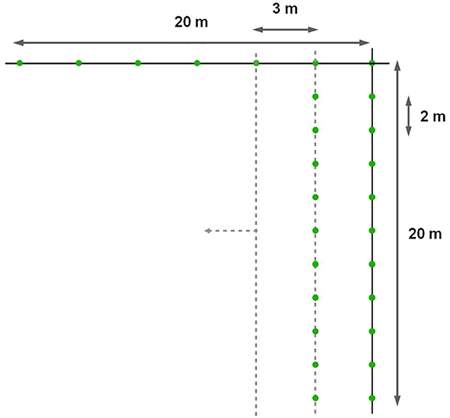
Fig. 2. Alignment layout applied in the planting stick method by using two wires (20 m). The three meters indicates space between the rows and the two meters indicates the space between planting spots.
Fig. 3. Photos showing a planting tube with a measuring rod used to indicate the correct distance between the seedlings (left panel), and a planter using marker sticks for correct alignment (right panel).
| Table 2. Cost factors used for both planting methods. |
| | Cost factor | Planting stick | Planting tube | Unit |
| Fixed cost | Purchase price of the tool | 8.00 | 141.30 | € |
| Number of tools | 10 | 1 | |
| Purchase price of the iron wires per seedling basket | 10.70 | 48.00 | € |
| Total purchase price | 90.70 | 189.30 | € |
| Service life | 2 | 5 | a |
| Salvage value | 15 | 15 | % |
| Total salvage value | 13.60 | 28.40 | € |
| Interest on capital | 6 | 6 | % |
| Variable cost | Hourly wage | 1.00 | 1.00 | € h–1 |
| Number of workers | 10 | 1 | Person per method |
| Duration of a working day | 8 | 8 | Hours day–1 |
| Number of working days | 120 | 120 | Days year–1 |
| Table 3. Productivity of the planting stick method, performed by a group of workers, and average time for each work element. |
| Planting stick | Work element | s seedling–1 |
| Moving | 0.59 |
| Aligning | 0.78 |
| Preparation | Subtotal | 1.37 |
| Walking | 4.39 |
| Preparing | 4.82 |
| Planting | 3.12 |
| Tamping | 2.90 |
| Planting | Subtotal | 15.23 |
| Total | 16.60 |
| Table 4. Productivity of the planting tube method, performed by one person. The preparation time was calculated for a planting row, which consisted of 48 seedlings. |
| Planting tube | Work element | s seedling–1 |
| Measuring | 0.29 |
| Walking | 0.08 |
| Locating | 0.09 |
| Moving | 0.59 |
| Preparation | Subtotal | 1.05 |
| Walking | 3.01 |
| Preparing | 3.24 |
| Planting | 2.4 |
| Pulling up | 1.37 |
| Tamping | 7.03 |
| Navigating | 2.90 |
| Planting | Subtotal | 19.95 |
| Total | 21.00 |
| Table 5. Fixed, variable, hourly, and unit costs of the two planting methods, based on the productivity study and cost calculation. |
| | Planting stick | Planting tube |
| Fixed costs, € h–1 | 0.0446 | 0.0413 |
| Variable costs, € h–1 | 9.99 | 1.00 |
| Hourly cost, € h–1 | 10.04 | 1.04 |
| Unit cost, € seedling–1 | 0.0463 | 0.0061 |
| Table 6. Results of REBA evaluation of work-related stress incurred using the planting stick method. Values in the ‘additional’ row include waiting time. The letter n in the first row indicates the respective number of observations. |
| Work phase | Work element | Negligible | Low | Medium | High | Very High | Total |
| % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n |
| Preparation | Moving | | | 9.5 | 6 | 14.3 | 9 | | | | | 23.8 | 15 |
| Aligning | 27.0 | 17 | 39.7 | 25 | 6.3 | 4 | 3.2 | 2 | | | 76.2 | 48 |
| Total | 27.0 | 17 | 49.2 | 31 | 20.6 | 13 | 3.2 | 2 | | | 100 | 63 |
| Planting | Walking | | | 23.1 | 24 | 4.8 | 5 | | | | | 27.9 | 29 |
| Preparing | | | 1.0 | 1 | 16.3 | 17 | 3.8 | 4 | | | 21.1 | 22 |
| Planting | | | | | 3.8 | 4 | 20.2 | 21 | | | 24.0 | 25 |
| Tamping | | | 5.8 | 6 | 5.8 | 13 | | | | | 18.3 | 19 |
| Additional | | | 8.7 | 9 | | | | | | | 8.7 | 9 |
| Total | | | 38.5 | 40 | 37.5 | 39 | 24.0 | 25 | | | 100 | 104 |
| Table 7. Results of REBA evaluation of work-related stress for the planting tube method. Values in the ‘additional’ row includes addition of seedlings to a container. |
| Work phase | Work element | Negligible | Low | Medium | High | Very High | Total |
| % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n |
| Preparation | Measuring | | | 15.2 | 7 | 19.6 | 9 | 4.4 | 2 | | | 39.2 | 18 |
| Walking | 8.7 | 4 | 2.2 | 1 | | | | | | | 10.8 | 5 |
| Locating | 8.7 | 4 | 8.7 | 4 | | | | | | | 17.4 | 8 |
| Moving | 32.5 | 15 | | | | | | | | | 32.6 | 15 |
| Total | 49.9 | 23 | 26.1 | 12 | 19.6 | 9 | 4.4 | 2 | | | 100 | 46 |
| Planting | Navigating | 1.4 | 2 | 9.4 | 13 | 0.7 | 1 | | | | | 11.5 | 16 |
| Walking | 2.2 | 3 | 10.1 | 14 | 0.7 | 1 | | | | | 13.0 | 18 |
| Preparing | 2.2 | 3 | 10.1 | 14 | 9.4 | 13 | | | | | 21.5 | 30 |
| Planting | 3.6 | 5 | 6.5 | 9 | 7.2 | 10 | | | | | 17.3 | 24 |
| Pulling up | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Tamping | 3.6 | 5 | 15.8 | 22 | 13.7 | 19 | | | | | 33.1 | 46 |
| Additional | 2.9 | 4 | | | 0.7 | 1 | | | | | 3.6 | 5 |
| Total | 15.8 | 22 | 51.8 | 72 | 32.4 | 45 | | | | | 100 | 139 |


