Fig. 1. The excavator-based harvester used for the research.
| Table 1. Specifications of excavator-base and harvester head used in the study. |
| Component | Specification |
| Base machine |
| Make and model | Sumitomo SH210 |
| Weight | 20 000 kg |
| Power rating | 117.3 kW |
| Width | 2800 mm |
| Length (without boom) | 4810 mm |
| Height | 2960 mm |
| Ground clearance | 440 mm |
| Boom outreach | 8700 mm |
| Head |
| Make | Waratah 616 C |
| Weight | 1680 kg |
| Max cutting capacity | 55 cm |
| Saw bar length | 75 cm |
| Number of feed-rollers | 3 |
| Feed-roller type | steel with angled bars |
| Number of knives | 2 fixed, 3 moving |
| Hydraulic fluid requirement | 320 – 360 l/min |
| Max hydraulic pressure requirement | 35 MPa |
| Table 2. Site description. |
| Plantation | Sappi Venus |
| Compartment | A44 |
| Species | E. grandis (Coppiced) |
| Area (ha) | 42.0 |
| Age (yrs) | 11.0 |
| Average DBH (cm) | 21.0 |
| Average Height (m) | 33.7 |
| Spacing (m) | 2.4 × 2.4 |
| Trees per hectare (after mortality) | 1383 |
| Average tree volume (m3) | 0.466 |
| Removal per hectare (m3) | 645 |
| Original sample size (trees) | 769 |
| Ground roughness | Smooth |
| Slope | Level to Gentle (less than 20%) |
| Table 3. Description of time elements of the cutting process. |
| Time element | Description |
| Moving | Any time the tracks were rolling. |
| Felling | Positioning the harvester head around the standing tree, which began when the boom reached out; felling proper, which began when the chainsaw started advancing and ended when the tree started to fall and the head was horizontal, ready to process the tree. |
| Processing | Began when the head was horizontal and included delimbing, debarking and crosscutting. Ended when the last assortment had been processed. |
| Other work | Any other productive time (e.g., removing of obstacles, stacking logs etc.). |
| Delays | Non-productive time, including mechanical, operational and personal delays. |
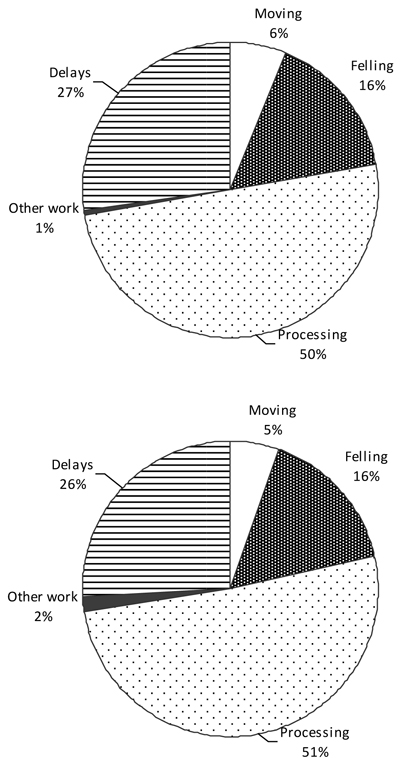
Fig. 2. Breakdown of worksite time by activity type for single stems (above) and double stems (below).
| Table 4. Multiple regression models for time consumption. |
| Moving |
| T = | 5.147 |
| Felling | R2 adjusted = 0.428 |
| Ln T = a + b DBH^2 + c OPB |
| | Coeff | SE | T | P |
| a | 2.149 | 0.031 | 68.635 | < 0.001 |
| b | 9.389 * 10–4 | 0.511 * 10–4 | 18.381 | < 0.001 |
| c | 0.217 | 0.048 | 4.526 | < 0.001 |
| Processing (= delimb, debark, cross cut) | R2 adjusted = 0.715 |
| T = a + b DBH^2 + c OPB + d OPB * DS |
| a | 19.672 | 1.038 | 18.942 | < 0.001 |
| b | 0.057 | 0.002 | 33.871 | < 0.001 |
| c | 4.942 | 2.431 | 2.032 | 0.043 |
| d | 6.653 | 2.991 | 2.224 | 0.027 |
| Cutting (= felling + processing) | R2 adjusted = 0.750 |
| T = a + b DBH^2 + c OPB + d OPB * DS |
| a | 26.516 | 1.227 | 21.612 | < 0.001 |
| b | 0.074 | 0.002 | 36.944 | < 0.001 |
| c | 9.038 | 2.863 | 3.157 | 0.002 |
| d | 7.295 | 3.521 | 2.072 | 0.039 |
| Other work |
| T = | 1.168 |
| Delays |
| (Moving + Cutting + Other work) * 0.208 |
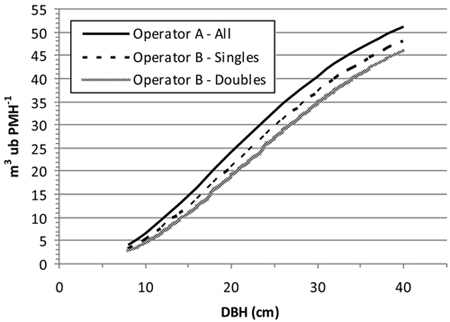
Fig. 3. Harvester productivity as a function of tree size and treatment (single vs. double stem). DBH = Stem diameter at breast height (1.37 m).